Like the majority of server systems you will install your SSL certificate on the same server where your Certificate Signing Request (CSR) was created. This is because your private key will always be left on the server system where the CSR was originally created. With Microsoft systems the private key is hidden away and will only appear once the CSR request has been completed. Your SSL certificate will not work without this private key file.
Majority of Azure clients create this keypair from a Windows IIS system. They would install the certificate back into the IIS system, Export and Import it into their Azure Account. We will assume that this is the case and the original system.
If you already have your PFX file refer to Step 4 of these instructions.
To Install your SSL certificate on Windows Azure perform the following.
Step 1: Picking up your SSL Certificate:
- If you had the option of server type during enrollment and selected IIS you will receive a pkcs#7/.p7b version of your certificate within the email. Alternately you can access your Certificate User Portal by the supplied link in the email to pick up the pkcs#7 version of your certificate.
- Copy the SSL certificate and make sure to copy the —–BEGIN CERTIFICATE—– and —–END CERTIFICATE—– header and footer Ensure there are no white spaces, extra line breaks or additional characters. Use a plain text editor such as Notepad, paste the content of the certificate and save it with extension .p7b (When performing this on a Windows system the Icon of the file should change into a certificate icon)
Step 2: Installing your SSL certificate:
- Open your IIS Manager. Choose Start > Administrative Tools > Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
- From the left menu, Click the server name.
- In the middle pane, under Security, double-click Server Certificates.
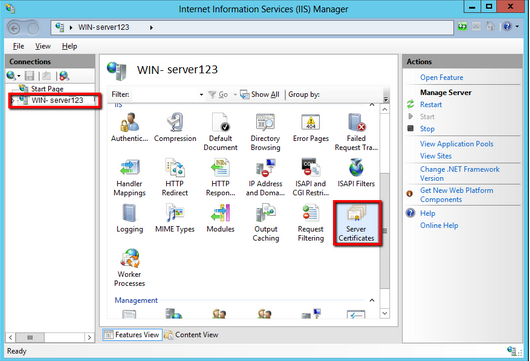
- From the right Actions pane, select Complete Certificate Request.
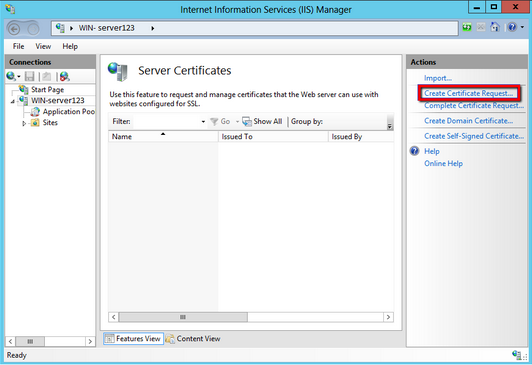
- Click on the
 button, navigate and select the location of your new certificate file. (change the file type you are searching for to all .p7b as the default type may be .cer)
button, navigate and select the location of your new certificate file. (change the file type you are searching for to all .p7b as the default type may be .cer) - Specify a friendly name for quick identification of your new certificate.
- Click Ok.
Note: You may receive an error when the system is performing the install. This is typically with a glitch with the IIS 7 to 8 series.- Click Ok to acknowledge the error message, and Cancel out of the Complete Certificate Request Wizard.
- Hit F5 on your keyboard to refresh the IIS console. Your new certificate should appear in the Middle pane under Server Certificates. It might be missing a friendly name. If you see the new certificate in this pane it means that installation was successful.
Note: If you certificate still does not appear then either the CSR request was never created on this system, or your private key was damaged. You will have to generate a new CSR request and perform a reissue of the certificate.
Step 3: Exporting your certificate:
- Start > run > MMC.
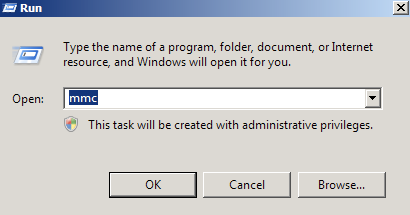
- Go into the Console Tab > File > Add/Remove Snap-in.
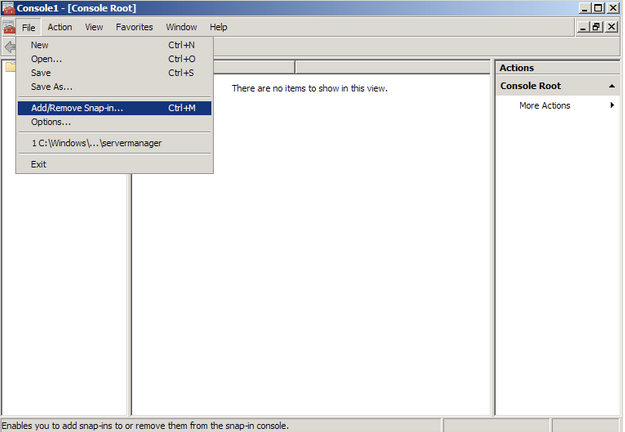
- Click on Add > Click on Certificates and click on Add.
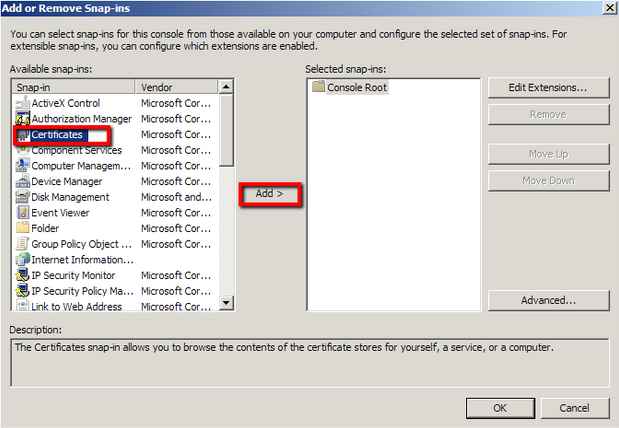
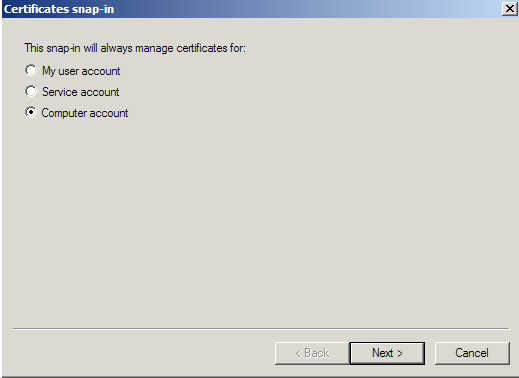
- Choose Computer Account > Next.
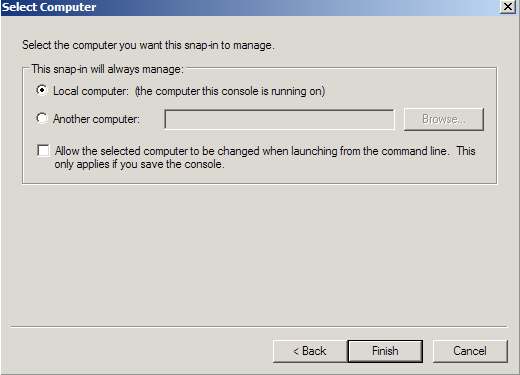
- Choose Local Computer > Finish.
- Close the Add Standalone Snap-in window.
- Click on OK at the Add/Remove Snap-in window.
Step 2: Export/Backup certificate to .pfx file:
- In MMC Double click on Certificates (Local Computer) in the center window.
- Double click on the Personal folder, and then on Certificates.
- Right Click on the Certificate you would like to backup and choose > ALL TASKS > Export.
- Follow the Certificate Export Wizard to backup your certificate to a .pfx file.
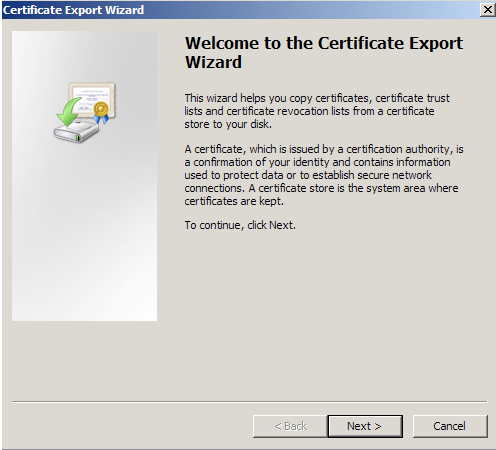
- Choose to ‘Yes, export the private key‘
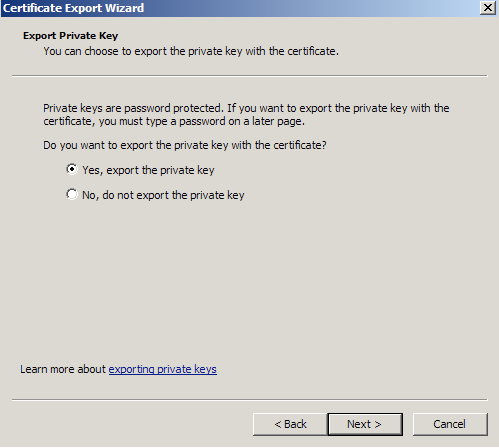
- Check Include all certificates in certificate path if possible. (do NOT select the delete Private Key option)
- Enter a password you will remember.
- Specify a file name and path by clicking on the
 to save your file.
to save your file. - Click Finish.
- You will receive a message > “The export was successful.” > Click OK.The .pfx file backup is now saved in the location you selected and is ready to be moved into your Azure Account.
Step 4: Importing and Assigning certificate pfx into Azure account:
- Log into the Azure Management Portal.
- Click on Cloud Service or Web App you wish to configure and then select the CONFIGURE tab.

- Under certificates click upload a certificate.
- On the Upload a certificate window click
 and browse to your pfx file that you had saved in Step 2.
and browse to your pfx file that you had saved in Step 2. - Specify the password for the pfx file you had created.
- Click on the
 to confirm.
to confirm.
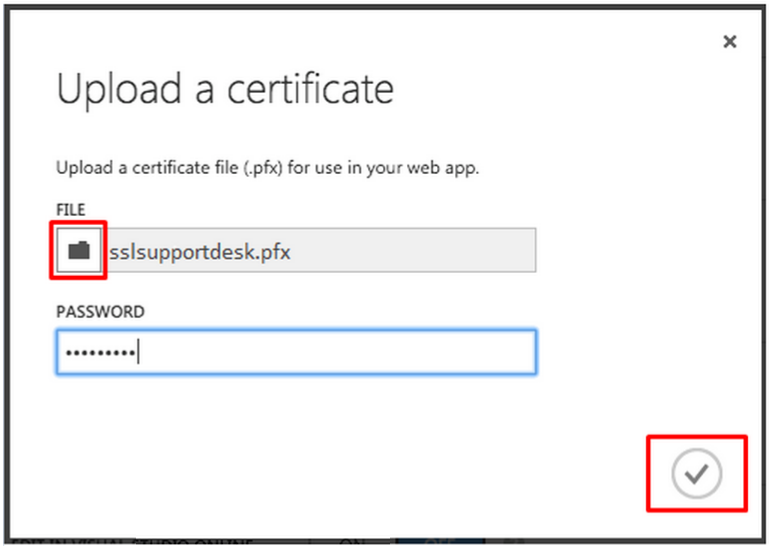
After Upload your SSL certificate will be available under the “Certificates” section. - Under ssl bindings, In the Choose a domain name drop-down list, specify the domain that you want to secure with SSL.
- In the Choose a certificate drop-down list, select the new SSL Certificate that you want to use to secure your website.
- Select whether to use Server Name Indication (SNI) or IP based SSL.
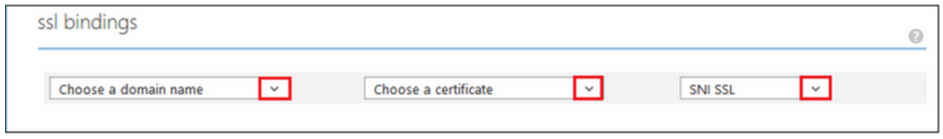
- IP based SSL: associates a certificate with a domain name by mapping the dedicated public IP address of the server to the domain name. This requires each domain name (domain.com, www.mysite.com, etc.) associated with your service to have a dedicated IP address. This is the traditional method of associating SSL certificates with a web server.
- SNI based SSL: is an extension to SSL and Transport Layer Security (TLS) that allows multiple domains to share the same IP address, with separate security certificates for each domain. Most modern browsers (including Internet Explorer, Chrome, Firefox and Opera) support SNI, however older browsers may not support SNI. For more information on SNI, see the Server Name Indication article on Wikipedia.
- Click Save to save the changes and enable SSL.Your SSL certificate is now installed and configured for its website.
If you are unable to use these instructions for your server, Acmetek recommends that you contact either the vendor of your software or an organization that supports Microsoft.
Microsoft Support:
For more information refer to Microsoft Azure.



